How is blockchain changing Cross-border payments? Explained.
Introduction
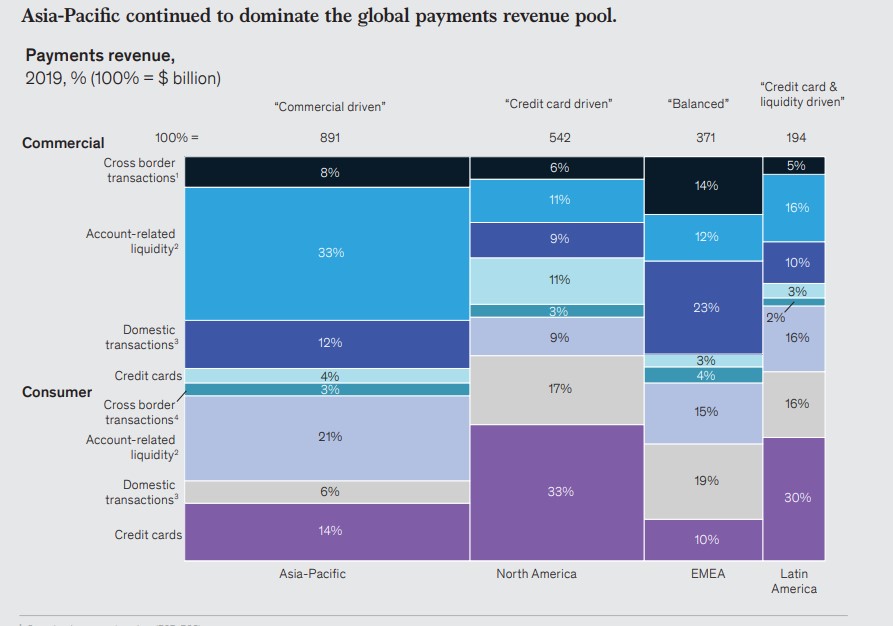
Cross-border payment is one part of the banking sector that has yet to benefit from recent progress in digitalization. Globally more people becoming digital buyers, cross-border payment is going to get evolution a lot. Cross-border payments revenues were estimated to reach $1.9 billion by the end of 2020, as reported. While pandemic seems to have reset the global payments landscape, cross-border payment getting more developed.
Consignments like import-export of unique items are the second-largest source of income for poor countries, contributing more than capital flows and development help. Countries such as Brazil, Indonesia, India, Thailand, are poised for a strong opportunity for payments growth.
What are cross-border payments?
With cross-border E-Commerce increasing, it's important that businesses can accept payments from their customers across the globe
By 2022, it is estimated that cross-border shopping will amount to $630 billion and make up 20% of e-commerce sales
It is also set to expand its reach, spanning at least 29 countries over the regions of North America, Latin America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Africa and the Middle East. If you are a merchant operating internationally, it is crucial that you can accept payments across all the countries that you are targeting.
So, coming back to the point, what are cross-border payments? Cross-border payments are transactions where the payer and the transaction recipient are based in separate countries. The transactions can be between individuals, companies, or banking institutions that are looking to transfer funds across territories.
To accept cross-border payments, merchants will need to work with a payment service provider who can process a wide range of payment methods. E-merchant pay is a payment service provider offering local and global payment methods.
Credit and debit cards, bank transfers, and local payment methods can all be used to make cross-border payments. Credit and debit cards are a go-to option for many consumers who are looking to make a cross-border payment, as they simply enter their card details and wait for the transaction to be approved.
International bank transfers are another way of placing cross-border payments. Consumers will need the merchant's IBAN and BIC to complete this type of transaction. Local payment methods, such as e-wallets, can also facilitate international transactions.
Customers like to pay in a way that is convenient and familiar to them.
Therefore, it's worth researching preferred payment methods in the territories you are targeting.
International payments normally take between two and five business days to clear. The more financial institutions that the payment has to pass through, the longer the transaction will take to clear. Soon, real-time cross-border payments will be adopted on a wider scale, with methods like Visa Direct and SWIFT gpi gaining popularity.
Another feature coming soon, that will make cross-border payments more efficient, is Secure Customer Authentication. Once implemented, payments made within the European Economic Area will have to go through a two-factor authentication process to verify the identity of the cardholder. Merchants should work with a payment service provider who offers
- Timely payment processing
- Transparent fee structures,
- A secure global payment gateway,
- A range of local payment methods and settlement currencies.
How is Blockchain changing cross border payment?
The concept of bitcoin has been around for a while now. It started in 2008 and the white paper. That is the paper that describes how bitcoin should actually function is titled as bitcoin a peer-to-peer electronic cash system, if you read it carefully, it talks bitcoin in an electronic cash system, so technically it's not exactly an investment product.
In fact, if you read the bitcoin white paper, you realize that the word investment is not at all used anywhere instead if you check out the word payments. it has been used frequently in the white paper. the white paper does not treat bitcoin to be an investment product, it essentially treats bitcoins to be a Payments product. It also talks about what are the flaws that are there in the present-day electronic cash systems and how bitcoin can change those flaws? How bitcoin can address those flaws?
So if you carefully look at bitcoin, the structure of bitcoin you realize bitcoin is more about payments and less about Investments
**now, payments can be divided into two categories: **
- National payments that take place within the borders of one country, there is no multi-currency involved in national payments
- International payments or cross-border payments usually take place between two nations between two countries.
Having different currencies and that's why most of these payments are multi-currency exchanges, you not only transfer the money but while transferring the money, you also have to change the currency of that money and that's the reason international payments are considered being expensive and very slow a simple google search will tell you it takes about two to five working days to have an international transaction take place and according to the World Bank the average cost of sending this money between the nation is around 7% of the total transaction value of the primary reason for this is lack of trust. A bank in one country does not trust a bank in another country, and therefore it's not able to transact freely and quickly, a bank in one country cannot really rely on the data that is being provided by a bank in another country and that's the reason there is so much friction in international payments
The question is, whom do you trust?
Therefore, what you basically do is you build a network you may depend on a few banks outside the country, those banks will rely on other banks in other countries And so on and so forth. That's how you built a banking network and because you have various banks connected to each other through various connections, there are various routes to send money around, so when an international transaction takes place, money travels through this network sometimes the banks may have a direct connection, so it's very easy to send and receive money it's also very cost-effective, but sometimes the connection is established through a series of banks therefore what ends up happening is that every bank through which money passes ends up charging a fee for processing the transaction this makes transactions not only slow but quite expensive too however there is a very simple mechanism to solve this problem
What if we just remove all these banks in between and just allow the first bank and the last bank to talk to each other?
Directly in a safe environment. If you remove all the middlemen from the equation, the fees drop significantly and the speeds can improve. Drastically, however, the main issue that props up by. removing these banks is how to do one bank in one country trust another bank in another country and that's where blockchain comes into the picture blockchain stores data in a tamper-proof manner using blockchain, the end banks that start and receive the transaction can directly communicate with each other without the need to rely on this banking network and banking channels, this not only reduces the cost of transferring money but drastically improves the speed at which money travels, so blockchain to a great extent is becoming very useful in processing these international transactions, but let's step back because in international transactions you have various banks and because of those various banks, you take more time and money
blockchain can solve that problem but for national payments, you don't really have a series of banks through which the money transacts every nation has its own payment infrastructure all the banks can directly communicate with each other within the national boundaries of a country they are protected by law, and therefore they can easily trust any random bank within that nation so blockchain's speed and cost are relatively faster compared to the options available in international markets but when you compare to the options available in domestic markets, it becomes very slow and very expensive to have a blockchain transaction so with international payments yes blockchain is being quite useful while conducting those transactions but with national payments, the benefits of blockchain do not add up much so you will be better off using the system that you are already using than to transition to a blockchain-based system.
The End!
I hope you found this article valuable. If yes, let me know in the comments 😊
Also, if you got questions ping me anywhere.